The Nerve Impulse Seen from Outside
Dexter M. Easton July 2000 ©
Next topic Previous topic Table of Contents
Topic 15: Stimulating arrangements; the stimulus artifact
In our experiment, the stimulator is at the observerís right, and the cathode ray oscilloscope (CRO) at the left. The impulse, generated by a stimulus to the proximal end of the nerve, will move toward the left (Fig. 14, 15). The physiological solution is an electrical conductor. Therefore an electric pulse applied between the two electrodes at the right in the bath will be recorded at the left by the CRO. That signal is the stimulus artifact, which is followed, after a delay, by the action potential. The current responsible can be visualized as lines from one stimulating electrode to the other. The stimulus artifact is present whether or not the nerve is in the tube, though its form may be altered by the electrical properties of the nerve. It is called an artifact because it is a product of human intervention and is not produced by the nerve.
The voltage drop seen as the stimulus artifact is only a small fraction of the voltage pulse delivered from the stimulator. For example, the dial on the stimulator might read 10 V, but the signal seen by the CRO is only 100 mV (0.1 V). The reason for this discrepancy can be understood from an equivalent circuit diagram representing the system. The total resistance of the path taken by the current is shown as 101000 ohms. The part of the path subtended by the recording electrodes is 100100/1000 of the total resistance. The voltage drop is proportional to the resistance, and the voltage seen by the CRO is therefore about 1/100 of that available at the stimulator.
Figure 15. Stimulation "equivalent circuit."
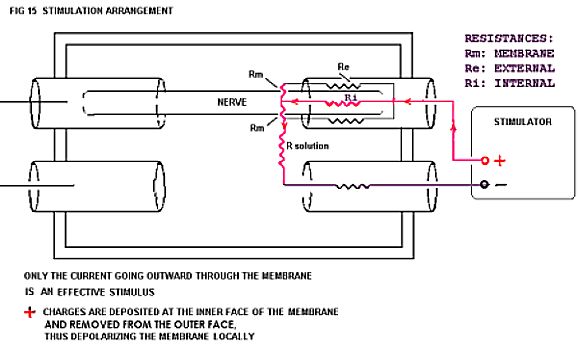
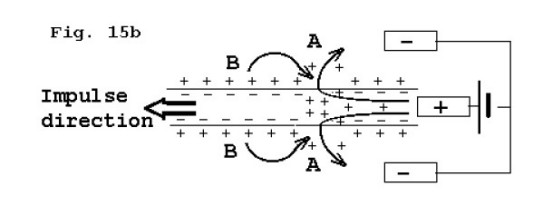

The end of the nerve in the stimulating tube receives positive (+) current. The positive charges moving into the nerve fiber reduce the negativity at the inside of the membrane relative to that at the outside. The region where the current flows out of the membrane therefore becomes depolarized. Conductance for Na+ and K+ ions increases at that point, and an impulse is born in each fiber that is depolarized to threshold.
Next topic Previous topic Table of Contents


