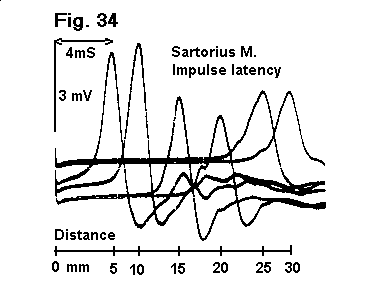
Fig. 34. AP recorded at increasing propagation distance.
The action potential is recorded at R, in Fig. 33, following a stimulus delivered at S. The scale shows the propagation distance in millimeters between stimulating and recording tubes (x in Fig. 32), corresponding to each AP peak. Time between stimulus artifact and AP peak increases with propagation distance. In each of the records, the upward spike is due to the leading-edge current detected when the peak of the impulse approaches the barrier and those currents flow through the gap. The downward deflection in each instance represents the trailing currents as the impulse peak enters the other side.